In Spring 2023, the Opus College of Engineering welcomed Mike Ahmad to campus as the Opus College’s new director of clinical engineering, specifically to lead programs and initiatives for the Marquette University and Medical College of Wisconsin Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering. Ahmad brings with him three decades of experience as a biomedical engineer and leader in the field of healthcare technology.
Ahmad currently leads the Opus College’s new Clinical Immersion in Medical Device Design certificate, and is collaborating with faculty, industry and clinical partners to imagine new educational offerings for professionals.
In a Q&A, Ahmad discusses his perspectives from the field, his current role and the exciting new opportunities ahead for professionals to learn from and work with the Marquette University and Medical College of Wisconsin Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering.
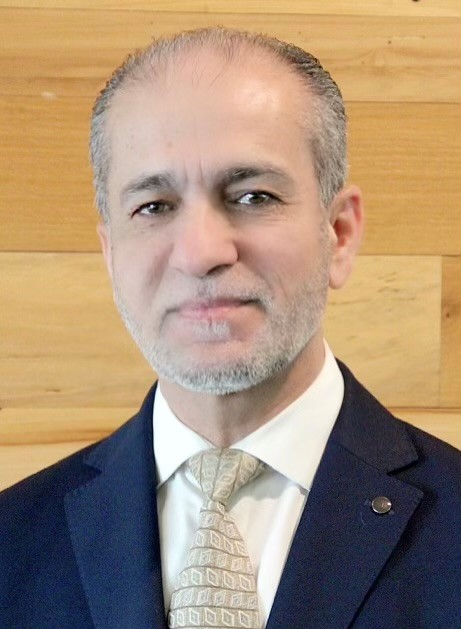

What work do you lead at Marquette?
As the director of clinical engineering, my role is focused on managing and overseeing the educational programs and resources related to clinical immersion in medical devices design and healthcare technology management, specifically through our Clinical Immersion in Medical Device Design certificate and future Healthcare Technology Management programs.
My responsibilities include program development, curriculum design, students advising as well as engaging with industry and clinical partners for new collaborations.
My role as the director of clinical engineering is essential in preparing future healthcare technology management professionals and contributing to the quality and safety of healthcare delivery through effective management of medical devices design and technology.
How do you see the role of a biomedical engineer changing today and in the future?
The role of a biomedical engineer is evolving rapidly in response to advances in technology, healthcare deliverables, and the increasing complexity of medical challenges.
Here’s how I see the role of a biomedical engineer changing today and in the future:
- Integration and interoperability of technology and data
- Biomechanics and prosthetics
- Ethical and regulatory considerations
- Interdisciplinary collaborations
The role of a biomedical engineer is becoming more dynamic and interdisciplinary, driven by technological advancements and the evolving healthcare landscape. Biomedical engineers will continue to be at the forefront of innovations that improve patient care, enhance medical research and contribute to the overall well-being of society.
How does the Marquette University and Medical College of Wisconsin Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering aim to support these changing industry and talent needs?
We aim to support changing industry and talent needs by adapting programs, curriculum and resources to ensure that graduates are well-prepared for the evolving demands of the healthcare technology and biomedical engineering sectors.
We are revising curriculum, taking an interdisciplinary approach between two institutions, creating flexible degree paths and stackable certificates, and focusing on hands-on experiences and real clinical immersions. At the forefront of this effort is our engagement with industry and clinical partners to ensure our work is aligned to their needs.
The Marquette University and Medical College of Wisconsin Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering aims to produce graduates who are not only technically proficient but also adaptable, innovative and well-prepared to meet the evolving needs of the healthcare technology and biomedical engineering industries. This approach ensures that students can make meaningful contributions to the field and drive improvements and advancements in healthcare technology.
The Joint Department currently offers a Clinical Immersion in Medical Device Design certificate. What differentiates the experiences offered to professionals in that program?
The experiences offered to professionals in the Clinical Immersion in Medical Device Design certificate program differs from traditional academic experiences or industry training by providing a unique blend of hands-on clinical exposure, interdisciplinary collaboration and specialized skills development tailored specifically to the field of medical device design. I direct the program as a Subject Matter Expert and students experience a customizable curriculum. Ultimately, the certificate is built upon direct access to healthcare facilities.
This hands-on practical approach sets this programs apart from other traditional academic or industry training programs.
How is the program designed to be flexible for professional students?
This certificate is designed to be flexible for professional students in several ways to accommodate their busy schedules, diverse backgrounds and career goals. This includes asynchronous learning, accelerated options, the ability to stack credits from certificates into a full degree, and focusing on industry-relevant content.
Overall, the program is designed to accommodate the needs of working professionals, enabling them to advance their careers, acquire new skills and stay up to date with industry trends while maintaining their current professional commitments.
What types of organizations and professionals are you interested in collaborating with in the future?
As we lead our current programs and develop new offerings, I am interested in collaborating with healthcare facilities, biomedical and clinical engineering professionals, medical device manufacturers, regulatory agencies, professional associations and more.
Collaboration with these organizations and professionals can enhance the effectiveness of healthcare technology management, improve patient care, reduce costs and ensure compliance with regulations and best practices in the field. It also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within healthcare facilities and the broader healthcare industry.